The tiresome topic Carbohydrates frustrates you? Then you are certainly not alone, because this general confusion is a phenomenon that plagues the majority of all fitness athletes. Ask one of your friends and they will almost certainly tell you that carbohydrates are evil and that you should avoid them at all costs. Then ask another friend and she will tell you exactly the opposite. The reason for this disagreement is the amount of divergent information that can be found on the internet, which is sometimes used to promote certain products and fitness programs to women and men. Consequently, in this article we have set ourselves the goal of providing clarity in this regard and dispelling five major myths.
One thing first:
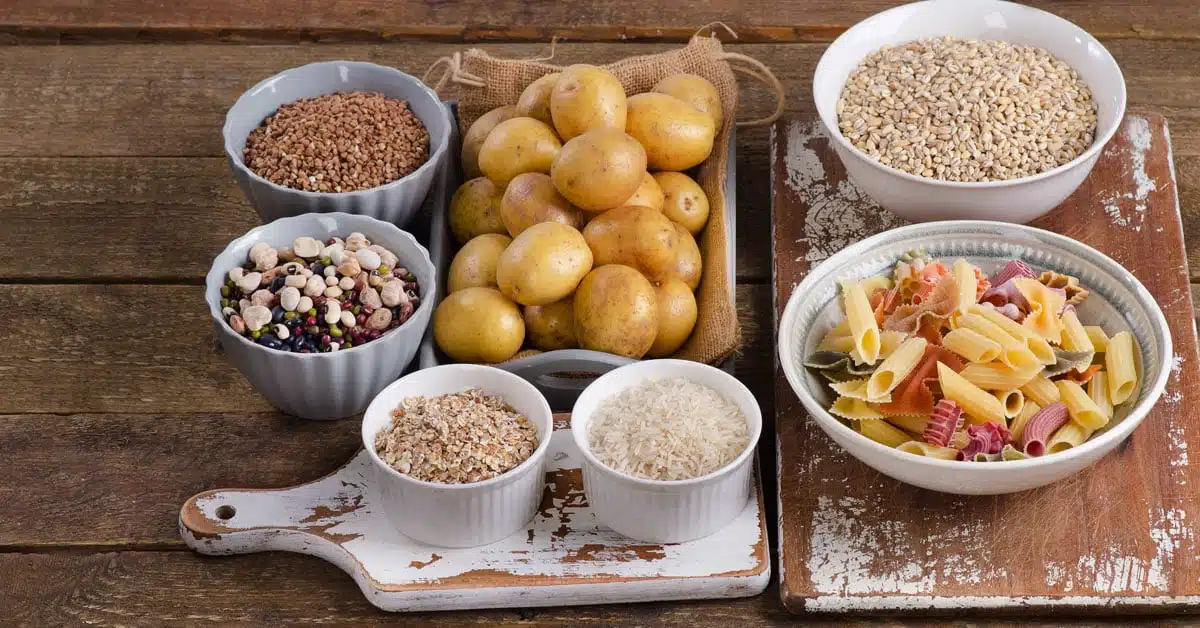
Alongside protein and fat, carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients that are essential for your body to function properly. Carbohydrates are broken down by your body into glucose, a simple sugar, which serves as a source of energy for all the activities you undertake throughout the day and is transported to your cells with the help of your blood. Even if someone has told you otherwise, carbohydrates are always part of a healthy and balanced diet. However, you should know that there are different types of carbohydrates that have an effect on your body due to their specific properties. In line with this fact, you should therefore pay particular attention to the quantities of certain carbohydrates you consume.
Myth 1 - Carbohydrates make you fat
The reason for this widespread myth is once again our society's preference for simple answers. We simply love not to deal with complex problems such as obesity in detail, but tend to blame a single nutrient. This culminates in statements like: Don't eat fat, don't eat sugar or don't eat red meat. Stupidly, carbohydrates per se have also ended up in this category, which is just as much nonsense. The truth is, quite simply, that many people simply eat too much, and it makes no difference in principle which macronutrients they contain. Nevertheless, carbohydrates are not entirely innocent, as short-chain carbohydrates in particular signal to our organism that they are an excellent source of energy from an evolutionary perspective. As a result, we tend to prefer to eat foods such as potato chips, cookies and ice cream, which contain a very high proportion of simple carbohydrates. If you want to prevent uncontrolled weight gain, you should therefore limit your consumption of these foods and opt for fruit, vegetables and wholegrain products instead.
Myth 2 - All short-chain carbohydrates are unhealthy
Short-chain carbohydrates have a bad reputation, as foods containing refined sugar are immediately associated with this form of carbohydrate. Although simple carbohydrates have a high glycemic index and cause blood sugar levels to rise, they are not necessarily unhealthy, as the carbohydrates contained in fruit and dairy products also have a short-chain molecular structure. The opposite is true for complex carbohydrates, which have a low glycemic index and have a significantly lower impact on blood sugar levels. One of the main influencing factors in this regard, which also ensures that the feeling of satiety lasts longer, is the fiber they contain. Foods such as grains, seeds, vegetables and other wholegrain products, for example, consist primarily of complex carbohydrates and fiber. Once again, the key to a healthy diet is to find a sensible level of consumption and not to consistently avoid something.
Myth 3 - Pasta and bread are bad for you
Although pasta and bread also contain a relatively high proportion of comparatively simple carbohydrates, this does not mean that these foods are bad for you. Once again, it depends on the size of the portions you eat. Furthermore, bread and pasta are part of everyday life for most people, which makes it understandably difficult to give them up. So if you are one of these people, you should make sure that you combine your pasta with particularly healthy foods such as vegetables, good oils and lean protein. A similar approach applies to bread, which you should also add the appropriate toppings to. The bottom line is that you don't have to give up anything completely, which makes it easier for you to achieve your goals in the long term, especially as part of a diet.
Myth 4 - Low-carb diets are the only way to lose weight
Low-carb diets with a high fat and protein content are ideal for getting rid of the last stubborn pounds at the end of a diet. However, they are by no means the only way to help you lose body fat effectively. In fact, your performance suffers from a lack of carbohydrates. One reason for this is that both your brain and your muscles need to be supplied from alternative energy sources. During ketosis, the body obtains a type of substitute carbohydrate from fats, which are used as an energy source instead of conventional carbohydrates. The bottom line is that a high concentration of ketones not only causes a drop in performance in many people, but also causes physical complaints such as headaches, bad breath and persistent nausea. So instead of cutting carbohydrates out of your diet completely, you should focus primarily on high-fiber carbohydrate sources.
Myth 5 - Less than half of your diet should consist of carbohydrates
The truth is that every person has different needs when it comes to the intake of nutrients. As carbohydrates are extremely important for our body, their proportion in the diet should also meet this requirement. In practice, it makes much more sense to determine guideline values for the consumption of fats and proteins and to fix the carbohydrate intake on the basis of these figures. Based on experience, it has proven useful for athletes to consume around two grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. With regard to the daily intake of fat, this recommendation varies between 0.8 and 1.2 grams per kilogram of body weight. However, the threshold of 0.8 grams should not be undercut, especially when dieting, as the body otherwise tends to release less stored fat. Once these two factors have been determined, you can fill up the rest of your daily diet with carbohydrates without any major concerns, provided you primarily rely on complex carbohydrates.